- Published 25 Aug 2022
- Last Modified 12 Feb 2024
- 7 min
Ball Bearings Guide
To help you choose the right bearing, we cover all the types, brands and sizes of ball bearings available.

Reviewed by David Carmichael, Solution Engineer (February 2022)
What are ball bearings?
Ball bearings are a type of rolling-element bearing used to reduce friction and guide rotating parts. They allow for the injection of motion between different parts and transmit energy for mechanical operation. This type of bearing uses balls to maintain the separation and distance between the bearing races. Ball bearings are designed to reduce rotational friction while supporting both radial and axial loads. They are primarily made from steel, but other materials such as ceramic and nylon are available.
Ball bearings are used in a wide range of applications within the power transmission and manufacturing industries. You will find ball bearings in everything from vehicles and white goods to agriculture and aerospace machinery. There are a wide range of bearing types and sizes to suit all applications. Roller bearings are a similar rolling-element bearing which feature cylindrical rollers for supporting heavier loads.
Different types of ball bearing
With a wide range of ball bearings available, it is important to choose the right type for your application. There are some common types of bearing, such as angular contact and deep groove, which offer different performance and characteristics. Here you will find information on these differences.
Each bearing type can also be open-style or closed/sealed. Open-style ball bearings are the most common variety. Shielded-style bearings feature metal shields on either one or both sides. The shield prevents dirt and debris from contacting and affecting the operation of the bearing. However, it also allows for the free flow of oil through the bearing for smooth operation.
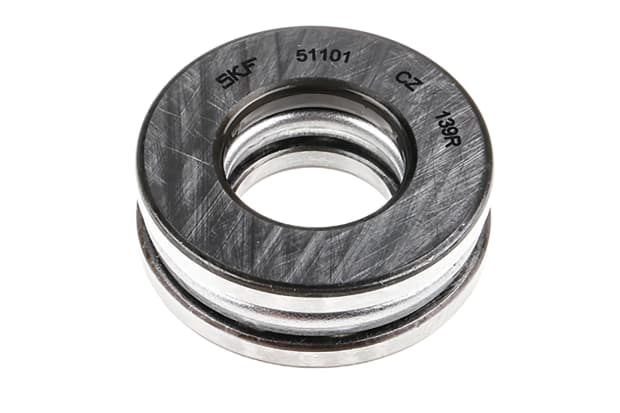

Thrust ball bearings
The thrust bearing is a unique variety of rotary bearing. As with other bearings, they facilitate interaction and movement between mechanical parts. However, their primary role is in the support of axial loads. Varieties of thrust bearings come complete with flat or aligning seats that correspond with the shape of the outer ring seat. Thrust bearings provide exclusive support for axial loads.
Thrust applications:
- Industrial fans
- Aerospace
- Automotive
- Mining
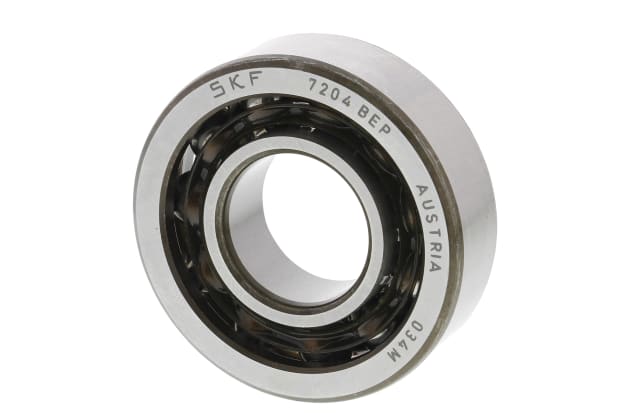

Angular contact ball bearings
Angular contact ball bearings feature internal and external ring raceways, which are disconnected from each other in relation to the bearing axis. These bearings allow for the support of loads with a combination of axial and radial forces. It is not possible to dismantle these bearings and remove the races or balls. However, they may feature a relatively large number of balls for increased support of axial and radial loads. Such bearings allow for the optimisation of speed and minimisation of friction specific to different loads. The three different types of angular contact bearings are single row bearings, double row bearings, and four-point contact bearings.
Angular contact applications:
- Compressors and pumps
- Metal rolling mills
- Electric motors and generators
- Machine tool spindles
- Vehicle hub bearings
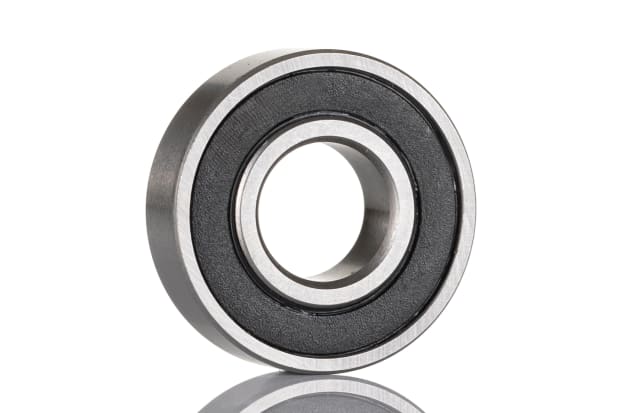

Deep groove ball bearings
Deep groove ball bearings are the most commonly used variety of ball bearings and can be purchased in seal, shield, and snap-ring arrangements. The race dimensions within these kinds of bearings closely match the dimensions of the balls that are contained. They are also well suited to the support of weighty loads. Deep groove bearings provide both radial and axial support. However, the contact angle can’t be adjusted in order to vary the relative levels of such loads. Types of deep groove ball bearings include single row deep groove bearings, extra small and miniature bearings, maximum type ball bearings, and magneto deep groove ball bearings.
Deep groove applications:
- Electric motors
- Vehicle motors
- Office machinery
- Garden tools
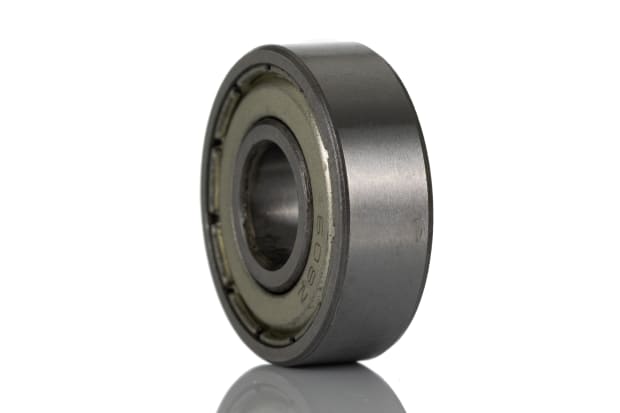

Miniature ball bearings
Miniature bearings, otherwise known as instrument or micro bearings, have a nominal outside diameter of under 9mm. Small ball bearings have a nominal inner diameter of less than 10mm and an outer diameter upwards of 10mm. It is common for miniature and small ball bearings to be made from stainless steel due to the relatively low force of objects exerted upon them.
Miniature applications:
- Gyros
- Anemometers
- Flow meters
- Miniature gearboxes
- Small motors
- Radio controlled models
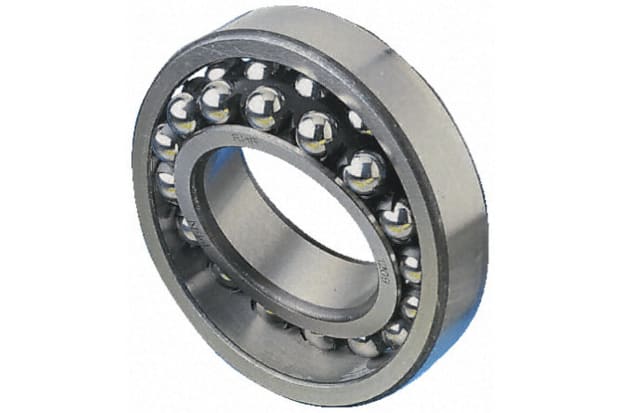

Self-aligning ball bearings
Self-aligning ball bearings feature an inner ring and ball assembly, which is held securely within an outer ring with a spherical raceway. The design of these ball bearings is such that they can tolerate a minor angular misalignment occurring as a result of either deflections or incorrect mounting. Such ball bearings are typically incorporated within long shafts due to the associated difficulty of properly mounting housing bores. It is also quite common for such bearings to be included in mechanical systems where there would otherwise be a risk of shaft bending during operation. However, the use of self-aligning bearings should be restricted to light axial load applications because the outer ring raceway provides a limited amount of support for the rolling elements.
Self-aligning applications:
- Gearboxes
- Final drive transmissions
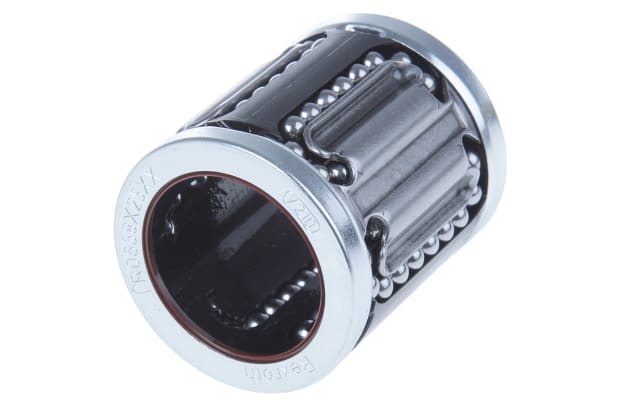

Linear ball bearings
Linear ball bearings are designed to provide free motion in one direction. They are the most widely used variety of linear slide and ensure a smooth precision motion along a single axis linear design. Featuring self-lubrication technology, these ball bearings allow for optimum performance and reliability. They are comprised of two linear ball bearing rows, integrated within four rods on alternate sides of the base.
Linear applications:
- Precise instrumentation
- Robotic assembly
- X-ray and imaging equipment
- Cabinetry
- Clean room environments
Popular ball bearings brands
Browse our most popular brands of ball bearings using the links below:
What are ball bearings used for?
There are two types of loads that have an impact on the function of the ball bearing; radial and axial. The radial load is projected around the radius and vertical force in relation to gear trains (ninety degrees to the shaft). Axial loads project horizontal force upon the bearing (the same axis as the bearing i.e. along the shaft). The other type of load to account for is dynamic, referring to the combined effects of the radial and axial forces. Ball bearings have been included in the manufacture of everything from skateboards to hard drives for optimum performance and functionality. Their main applications include:
- Aerospace engineering
- Centrifugal pump production
- Motors
- Conveyors
- Cooling fans
- Robotics
FAQs
Will ball bearings reduce friction?
Yes, ball bearings are specifically designed to reduce friction. These bearings contain balls which have less surface contact and produce less friction than a flat surface would. The inner ring and outer ring have rolling friction instead of sliding friction. Therefore ball bearings are able to spin smoothly. Due to the point contact of the balls to the raceway, these bearings can take relatively low loads, but at higher speeds than roller bearings. Conversely, roller bearings take higher loads but at slower speeds.
Where are ball bearings used?
Ball bearings are commonly used in machinery but are also widely used across many industries. You can find roller bearings in household appliances through to automotive and aerospace applications.
When to replace ball bearings?
It is important to follow the lifespan advised by the manufacturer of your chosen ball bearing. It is also important to identify when a ball bearing needs replacing. For example, changes in noises such as humming or clicking. There are also visible signs such as vibrations or misalignment. Condition monitoring can greatly reduce the chance of consequential damage from failed bearings.
What are ball bearings made of?
Ball bearings are most commonly made from carbon steel, however, when anti-corrosion properties are required they can be made from 304 stainless steel. This is due to its durability and corrosion resistance. However, there are plastic ball bearings and ceramic hybrid bearings available too.
How do plastic ball bearings work?
Budget-friendly plastic ball bearings don’t require any external lubrication and are corrosion-resistant, given the use of glass or plastic balls. These relatively lightweight bearings are suitable for use in particularly harsh environments and are a common choice for workers within the medical and food industries. Other common materials for ball bearings include steel and stainless steel.