- Published 1 Feb 2023
- Last Modified 12 Feb 2024
- 7 min
A Guide to Roller Bearings
In this article, we will take a closer look at roller bearings, their applications, and the difference between roller and ball bearings.

Reviewed by David Carmichael, Solution Engineer (March 2023)
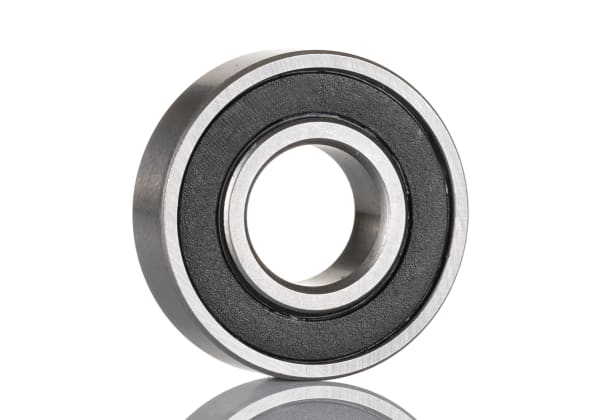
Roller bearings are a type of rotary bearing that uses rolling elements, typically cylindrical rollers, to support the load. These bearings are commonly used in a wide range of machinery and equipment, from automobiles and industrial machinery to household appliances and medical equipment. They are known for their durability, low friction, and high load-carrying ability.
What are Roller Bearings?
Roller bearings consist of an inner ring, an outer ring, and a set of rollers that are held between the two rings. The rollers are typically cylindrical but can also be tapered, spheroidal, or needle-shaped. The inner and outer rings are typically made of steel, while the rollers are made of steel or a harder material such as ceramic or tungsten carbide.
There are several types of roller bearings, each with unique characteristics and applications. The most common types include:
- Cylindrical roller bearings
- Needle roller bearings
- Spherical roller bearings
- Tapered roller bearings
The Applications of Roller Bearings
Roller bearings are used in a wide range of applications, including:
- Automotive: Roller bearings are used in the wheels, transmission, and engines of automobiles
- Industrial machinery: Roller bearings are used in a variety of industrial machinery, such as conveyors, fans, pumps, and gearboxes
- Medical equipment: Roller bearings are used in medical equipment, such as X-ray and MRI machines
- Household appliances: Roller bearings are used in household appliances, such as washing machines and refrigerators
- Agriculture: Roller bearings are used in a variety of agricultural applications, including tractors, combine harvesters, and other farm machinery
- Construction: Roller bearings are used in construction equipment, such as excavators, bulldozers, and cranes
The Difference Between Roller Bearings and Ball Bearings
The main difference between roller bearings and ball bearings is the type of rolling element used. Roller bearings use cylindrical rollers, while ball bearings use balls. Because of this, roller bearings can carry heavier loads and are better suited for applications where there is heavy radial or thrust loading.
Additionally, roller bearings typically have a higher load-carrying capacity and a lower speed rating than ball bearings. On the other hand, ball bearings are better suited for applications where there is high speed and low to moderate loading.
One of the most notable differences between roller bearings and ball bearings is that roller bearings are typically more expensive than ball bearings. However, they offer several advantages, including higher load-carrying capacity and increased accuracy.
Roller Bearings
Roller bearings are a type of bearing that uses cylindrical or needle-shaped rollers to support radial loads. They are designed to handle heavy loads and high speeds, making them ideal for use in a wide range of industrial and automotive applications.
Ball Bearings
Ball bearings are a type of bearing that uses steel balls to support radial loads. They are designed to handle moderate to high-speed applications and are commonly used in various devices, from household appliances to high-speed machinery.
How is Bearing Size Measured?
Bearing size is an important aspect of roller bearings and several factors determine the size of a roller bearing. These factors include the diameter of the shaft it will be mounted on, the bore diameter of the bearing, the outside diameter, and the width of the bearing.
The bore diameter is the inner diameter of the roller bearing and is typically measured in millimetres (mm). The width of the bearing is the distance between the outer races of the bearing and is also measured in millimetres.
To determine the proper size of a roller bearing where the shaft is the rotating element and the outer ring has a transition fit, the diameter of the shaft it will be mounted on must be known. The diameter of the shaft must be larger than the bore diameter of the bearing, as the bearing must fit snugly over the shaft. A tight fit is needed to prevent the bearing from rotating on the shaft, which could cause damage to the bearing and reduce its lifespan.
On the other hand, if the outer ring is rotating, then the housing must have a smaller diameter than the outer ring, and the shaft will have a transition fit.
In addition to the bore diameter and width, the load capacity of the bearing must also be considered when selecting the right size. The load capacity of a roller bearing is determined by the type of bearing, its size, and its material. For example, larger bearings can typically manage higher loads than smaller bearings.
It's also important to consider operating conditions, such as speed and temperature, as these can affect the size and load capacity of the bearing. In high-speed applications, for example, bearings with a low friction coefficient and high load capacity may be needed.
To ensure the proper functioning and longevity of a roller bearing, it is crucial to select the proper size based on the specific application requirements. It is also essential to select the correct lubrication for the conditions.
Roller Bearings Diagram

The diagram of a roller bearing typically includes the following components:
- The outer race: The outer ring of the bearing that sits on the outside of the assembly
- The inner race: The inner ring of the bearing that sits on the inside of the assembly
- The rollers: The cylindrical-shaped elements that roll between the races, allowing the bearing to rotate smoothly
- The cage: The separator that holds the rollers in place and prevents them from colliding with each other
- The seal: A barrier that prevents contaminants and lubricants from entering or exiting the bearing
The diagram of a roller bearing, like other types of bearings, can vary depending on the specific type of bearing and its design. For example, tapered roller bearings have a distinctive design compared to cylindrical roller bearings.
It's worth noting that the diagram is a simplified representation of roller bearing parts. The bearings are usually sealed and not visible in the machinery or equipment where they are used.
The Different Types of Roller Bearing
There are several distinct types of roller bearings available to meet specific application needs. Each type has unique features, benefits, and design specifications, making it a necessity to select the right type for each application.
In this section, we will take a closer look at the different roller bearing types. By understanding the key features and benefits of each type, you will be better equipped to make an informed decision when selecting roller bearings for your machinery and equipment.
Cylindrical Roller Bearings
Cylindrical roller bearings consist of an inner ring, an outer ring, and a set of cylindrical rollers that are held between the two rings. The cylindrical rollers are usually guided by a cage that separates the rollers and helps to distribute the load evenly.
Cylindrical roller bearings are designed to handle heavy radial and low-thrust loads. They are commonly used in industrial machinery, such as conveyors, fans, pumps, and gearboxes.
They come in several subtypes, including single-row, double-row, and multi-row cylindrical roller bearings. Single-row cylindrical roller bearings are the most basic type and are suitable for most standard applications, while double and multi-row bearings are designed to manage heavier loads.
Needle Roller Bearings
Needle roller bearings are a type of roller bearing that uses needle-shaped rollers. They are characterised by their small size and high load-carrying capacity.
Despite their small size, needle roller bearings can support heavy radial loads and are ideal for use in applications where space is limited. Common applications include domestic appliances, electric motors, and automotive transmissions.
Spherical Roller Bearings
Spherical roller bearings are a type of roller bearing that is capable of handling both heavy radial and thrust loads. They consist of an outer ring, an inner ring, and a set of spherical rollers that are held between the two rings. The inner ring has two raceways, and the rollers are shaped to match the raceways, supplying support and stability.
They are unique in that they are designed to accommodate misalignment and are commonly used in applications where shaft deflection or misalignment is a concern. Spherical roller bearings are commonly used in industrial machinery and construction.
Tapered Roller Bearings
Tapered roller bearings have a unique design. The rollers have a different diameter at each end, which creates a tapered shape. This design allows for a greater contact surface between the inner and outer races, making them ideal for handling heavy radial and thrust loads simultaneously.
They are a versatile choice, commonly used in automotive applications as well as industrial machinery. They are also suitable for use in applications where there is a need for precise shaft alignment and support for heavy radial loads.