- Published 5 Jan 2023
- Last Modified 29 Aug 2023
- 11 min
The Complete Guide To Robotic Parts

This guide is part of our Industrial Automation hub where you can discover more about AI, automation and control.
In this guide, we’ll look at some of the most familiar and popular types of robot parts and components sold, as well as identifying some of the different basic robot types and the sorts of roles they tend to perform in modern industry.
What are robotic parts?

As industrial robots have continued to evolve in complexity and functionality over the years, the extraordinary range of capabilities and roles they’ve become highly adept at performing has grown exponentially.
At the same time, even as the technology continued to advance throughout the course of the past decade, the manufacturing costs of many key components in robot design and construction - especially sensors - started to fall dramatically. The result, in industrial terms, has been a rapid expansion in the availability and affordability of robots and robotic parts across a very wide range of industries.
Robots and robotic elements of traditionally manual production processes are now far more commonly encountered - even in smaller-scale operations - than they once were, because they’re no longer so prohibitively expensive as to be viable only for businesses outputting at exceptionally high volumes and turnovers.
Regardless of whether they’re incredibly complex or relatively simple machines, all robots fundamentally consist of a few key parts that are common to any type. In short, in any programmable industrial robot there will always be:
- A controller acting as the ‘brain’ of the machine
- A series of mechanical parts and attachments designed to carry out the pre-programmed articulations
- Some assembly of sensors to help the robot fine-tune its performance in response to external stimulus
The ‘response to external stimulus’ mentioned in the last bullet point above is an important factor in defining robotics and robotic parts from other high-tech components. Interestingly, there isn’t really a very standardised consensus yet on what exactly constitutes a robot per se, as opposed to merely a machine capable of carrying out repetitive tasks to a consistent standard.
A key factor in identifying what we broadly consider ‘robotics’ is the ability of the machine to autonomously perceive and react to certain facets of its environment. It goes without saying, for example, that we wouldn’t typically consider a kettle to be a robot, even though it performs a repeatable task to a consistent standard with minimal input from us (beyond an initial instruction).
Many types of ‘smart’ technology now blur the lines between simple machinery and true robotics, thanks to their abilities to monitor and respond to changing parameters in their immediate environments. Again, this is due in part to the much more widespread and affordable manufacturing of sensor technologies today than was possible ten years ago.
Basic parts of a robot
As noted in the section above, the core parts of a robot are fairly consistent from model to model, regardless of the overall complexity of the machine they’re installed in. In essence, there will always be:
- A controller (usually a computer and software package) to deliver commands to the robot
- The physical structures and mechanical components that allow it to carry out the specified tasks (motors, pistons, wheels, housings and various other tools and ‘end effector’ parts)
- Various sensors, measuring devices and response-adjustable gauges to enable the robot to make sense of and respond to environmental factors that are instinctive for humans, such as direction, temperature, pressure, sizing and so on
The above is of course a very broad category list. In the sections below we’ll look a bit more specifically at some of the most frequently used robot parts, found in all manner of machines deployed across countless types of industrial and laboratory settings.
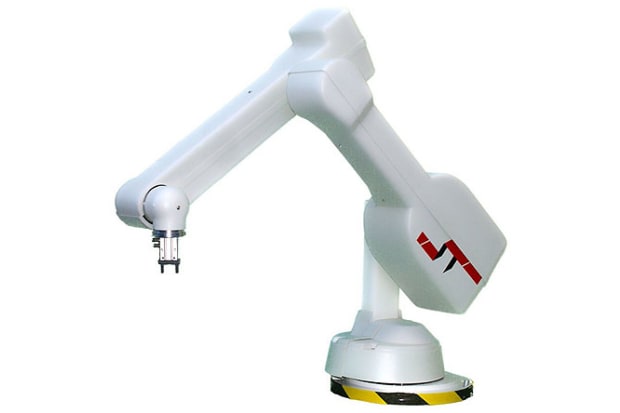
Robotic arms
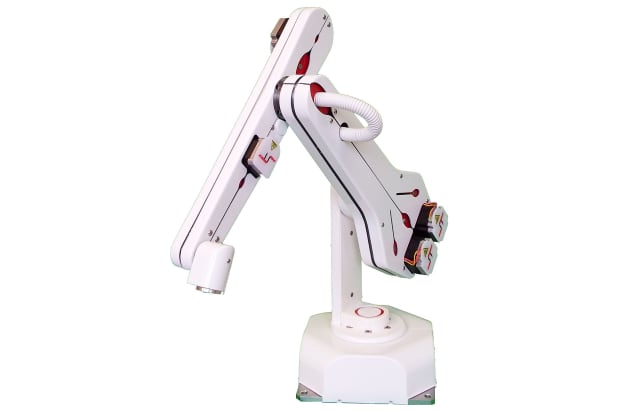

Robotic arms are machines that are programmed to execute a specific task or job quickly, efficiently, and extremely accurately. Generally motor-driven, they’re most often used for the rapid, consistent performance of especially heavy/delicate and highly repetitive procedures over extended periods of time. They’re especially valued in the industrial production, manufacturing, machining and assembly sectors.
Most robotic arms used for industrial production, assembly, or pick and place applications have 4-6 articulating joints designed to mimic the basic functionality of the human arm and hand. Common types of industrial, programmable robot arms include Cartesian, polar, cylindrical and SCARA arms, each of which operates within a differently shaped and coordinated ‘envelope’ of physical space in order to perform its main tasks - you can read more about each of these robot types at the end of this guide.
To explore this subject in greater detail, see our robotic arms guide.
Robotic controllers and control systems

Robotic controllers can take many forms, but in modern workplace uses they almost always involve a combination of hardware and software that together forms the digital computer system through which the robot is instructed and monitored.
As noted above, the closest human analogy here would be the brain - signals created and sent by the controller directly manage the movements of all other robotic parts, including joints, manipulators and any end effector attachments.
In essence, it is the robotic controller that makes a suitably equipped machine a robot, especially when working in combination with sensors that enable it to adjust automatically to external events and conditions.
Robotic control systems broadly fall into two overarching categories, namely:
- Pre-programmed control systems
- Simpler pre-programmed robots are designed purely to repeat the same basic operations over and over, and can only respond in very limited ways (if at all) to changes in the external environment. In other words, they require the maintenance of suitable conditions in which to perform its intended tasks properly.
- Autonomous robotic control systems
- More complex autonomous robots will be fitted with a range of sensors and other equipment that allow them to detect and respond to external factors or environmental changes.
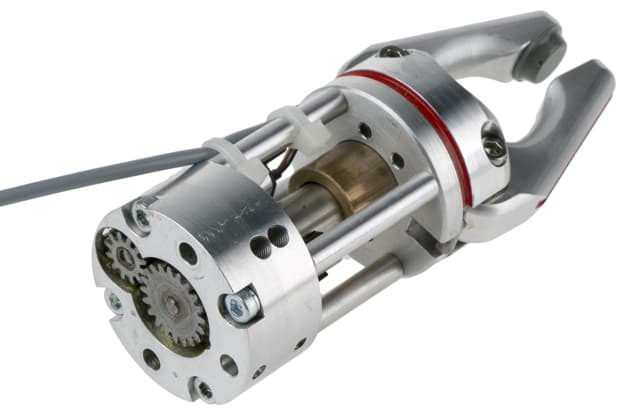
Robotic grippers
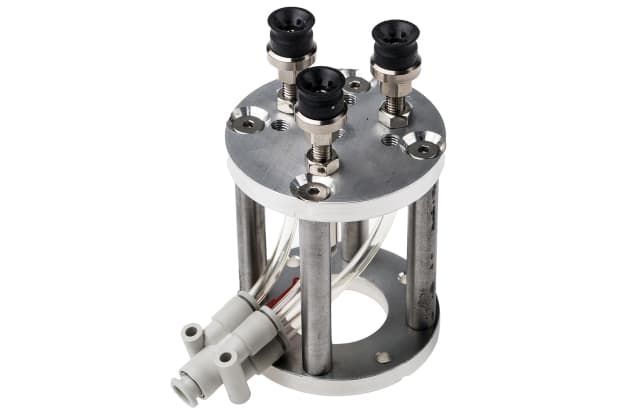

Grippers for robots are just one of many types of manipulator that can be fitted to the end effector (the ‘hand’) part of a robot or robotic arm, in order to provide it with certain key functions and abilities. Robotic grippers provide the machine with a means of achieving reliable purchase on a wide range of objects and components, which is essential for most production line, assembly and pick and place applications.
They’re usually designed either to be electrically operated, pneumatic, or based on vacuum principles - as with most robotic parts, the best solution for a given application will depend on the precise nature of the task and the specifics of the environment the robot is being put to work in.
Robotic joints and motors
Robotic joints and motors are what give these machines their prized ability to perform extremely precise, accurately repeatable movements again and again. There are a wide assortment of motors - also known as actuators - available for purchase from robotics suppliers, and picking out the right type will depend on consideration of a few key facts about the type and range of motion you want the robot to be able to perform.
The basic types of robotic motors available include:
- AC or DC motors
- useful for very high torque (AC motors) or high speed (DC motors) applications but DC motors, in particular, are not usually very strong unless modified with additional gears
- geared AC motors and geared DC motors are therefore also widely available
- Servo motors
- An AC, DC or brushless DC motor combined with a position-sensing device and a control circuit. A servo motor is a rotary actuator that allows for precise control of angular position. The motor is attached by gears to the control wheel, and as the motor rotates, the position sensors resistance changes, so the control circuit can precisely regulate movement.
- Often combined with a servo drive control, a type of electronic amplifier used to power and monitor the feedback from servomechanisms.
- Stepper motors
- A brushless DC electric motor that divides a full rotation into a number of equal steps. The motor’s position can then be made to move and hold at one of these steps without any position sensor for feedback.
- With a computer-controlled stepping, these motors can be used to achieve very precise positioning and/or speed control, ideal in very numerous robotics applications.
- Linear actuators
- Linear actuators create a straight line motion, and have been designed to withstand a wide range of operating conditions. Actuators work by converting energy produced by an electric motor into torque, which then moves a mechanism.
- The control system of an actuator can be handled mechanically, electrically, or through software.
Robotic sensors and transducers
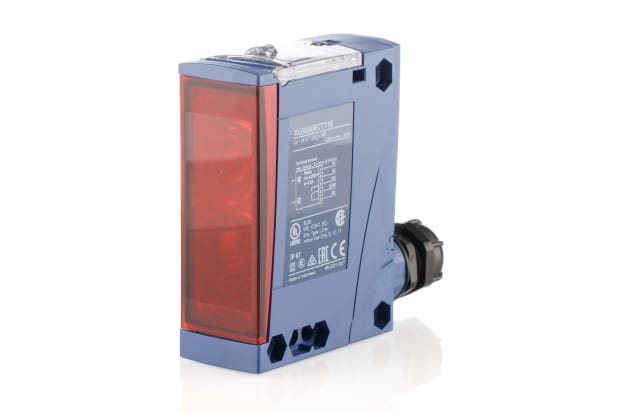

In terms of comparison to human abilities, robots can quite easily be fitted with a range of sensors, lenses and other add-ons that provide them access to many of the same basic senses we have - sight, hearing, touch, and so on. The trickier problem is teaching the robot how to understand and make sense of that data as it receives it.
The wide array of robotic sensors on sale can be broken down into various key categories, which might include:
- Contact sensors
- Push buttons and contact switches
- Pressure pads and sensors
- Distance sensors and gauges
- Ultrasonic range finders
- Infrared sensors
- Laser measurement devices and sensors
- Stretch and bend sensors
- Positioning sensors
- Room navigation (indoor localisation) sensors
- GPS and other live tracking devices
- Rotation sensors
- Potentiometers
- Gyroscopic devices
- Environmental sensors
- Photoelectric or light sensors
- Sound sensors
- Thermal sensors and thermal imaging cameras
- Humidity and moisture sensors
- Pressure sensors
- Gas sensors
Different types of robots
There are many different types of robots used in modern industries and workplaces. In this section, we’ll look at some of the more commonly found types, and the kinds of roles they tend to perform.
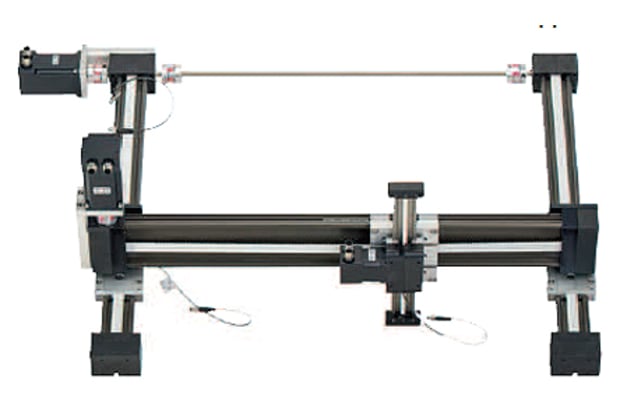

Cartesian robots
Cartesian robots are so-called because they operate based on the Cartesian coordinate system - in other words, their movement is plotted and controlled along the familiar X, Y and Z axes that we’re used to seeing on most graphs and 3D charts. They’re commonly found performing tasks such as machine tooling or picking and placement.
The joints and motors of Cartesian or gantry robots are therefore programmed using X. Y and Z coordinates to enable linear movement in these three dimensions, sometimes with the benefit of an additional rotating wrist joint for further flexibility. A series of linear actuators allows the Cartesian robot to position a tool or attachment accurately in three-dimensional space, and manipulate it through a series of linear movements to switch between positions.
Cylindrical robots
Cylindrical robots are programmed along a set of axes that allow it to perform its tasks within a cylindrical ‘work envelope’, which is the robotics design term for the size and shape of physical space the robot has the potential to manoeuvre within. As you’d expect, for cylindrical robots this work envelope is cylindrical in shape, meaning the robot can perform movements up, down, and around a central axis.
This is achieved through inclusion of both rotary and prismatic joints, giving the cylindrical robot the potential for both rotational and linear motion. This type of robot is widely used in applications such as spot welding and machine tool handling.
Polar robots
A polar or spherical robot is one that operates within a spherical work envelope, achieved through a combination of a rotational joint, two rotary joints, and a linear joint. The subsequent spherical workspace it has access to makes it useful for performing similar roles to those outlined above for cylindrical robotic arms, only with an increased ability to move back and forth within the work space - again, this will often mark the polar robot as especially well suited to handling machine tools, spot welding, die casting and arc welding applications.
SCARA robots
SCARA is an acronym that stands for Selective Compliance Assembly Robot Arm (or sometimes Selective Compliance Articulated Robot Arm). In the context of robotics, ‘compliance’ refers to a degree of allowable flexibility in movement, and SCARA robots are designed to allow for some small degree of flex in one or two directions of movement while remaining absolutely rigid along other axes. This can be especially useful in certain assembly or component placement tasks, where the benefit of selective compliance means that close-fitting parts can be slotted together without binding or damaging in tasks performed to very tight tolerances.
Product spotlights
Browse our most popular robotics and accessories product categories: